Why Soybean Oil May Be Harming Your Health: Inflammation, Omega-6 Risk & Heating Effects
Soybean oil faces criticism due to omega-6 imbalance, inflammation, and harmful compounds formed during heating. Learn how it affects metabolism, gut health, and hormones.
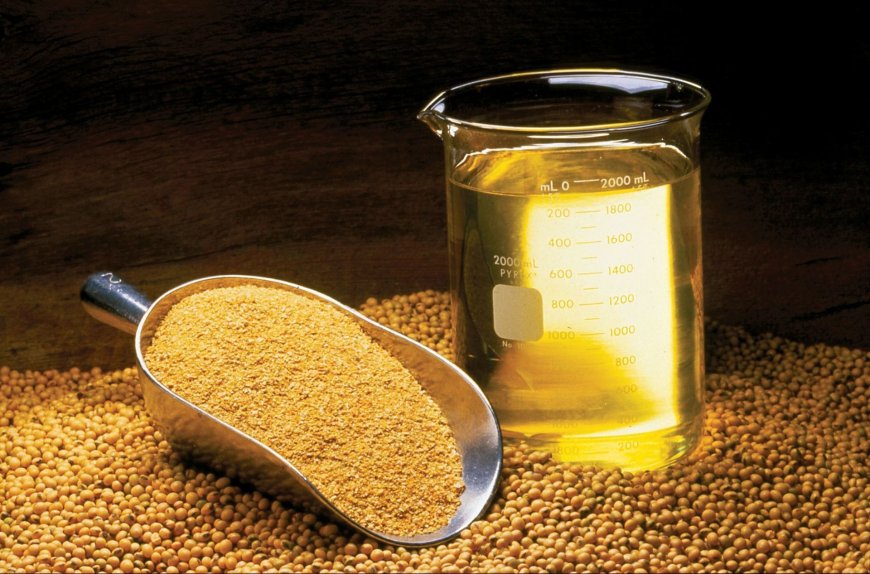

Soybean oil has recently come under scrutiny as a regular cooking medium due to concerns around its fat composition, inflammatory nature, and how it reacts when exposed to high heat. Many households adopted soybean oil because it is affordable, widely available, and aggressively marketed as a “healthy” choice. On the surface, it appears beneficial, as it contains omega-6 fatty acids, vitamin E, and low levels of saturated fat. However, modern nutritional science evaluates oils not just by labels, but by fat ratios, heat stability, and their impact on metabolism.
Soybean oil undergoes high-temperature chemical processing during extraction, which helps keep its cost low but significantly alters the structure of its fatty acids. This process can lead to oxidation, generating free radicals that place extra stress on the body. When used repeatedly for deep frying or high-heat cooking, the oil breaks down rapidly and produces harmful compounds linked to chronic inflammation.
The Omega-6 Imbalance Problem
While omega-6 fatty acids are essential, they must be consumed in balance with omega-3 fats. A healthy ratio is commonly considered to be around 4:1 or lower. Soybean oil, however, can push this ratio to an alarming 20:1, severely disturbing metabolic balance. Excess omega-6 intake promotes the formation of inflammatory compounds, which are associated with belly fat accumulation, joint pain, insulin resistance, and elevated triglycerides.
Given that most Indians already consume large amounts of omega-6 through bakery items, fried snacks, namkeen, and restaurant foods, soybean oil further worsens this imbalance.
What Happens When Soybean Oil Is Heated?
Indian cooking typically involves high temperatures through frying, tempering, and roasting. Although soybean oil has a moderate smoke point, the larger concern is its poor oxidative stability. Under intense heat, it forms lipid peroxides that damage cells and aldehydes that increase the risk of neurological and cardiovascular issues. Repeated heating can also generate traces of trans fats. These toxic by-products may not be visible in the pan, but they silently trigger inflammation in the body over time.
The Gut and Hormonal Impact
Recent studies suggest that soybean oil may affect gut health and hormone balance. Its omega-6-heavy composition can disrupt beneficial gut bacteria, influencing digestion, immunity, and appetite regulation. For women dealing with PCOS, thyroid disorders, or insulin resistance, this inflammation cycle may further aggravate symptoms.
What About Vitamin E?
Although soybean oil does contain vitamin E, a natural antioxidant, the quantity remaining after refining and cooking is often too minimal to counteract the oxidative damage caused by heating.
The bigger issue is not the soybean plant itself but the industrially refined, chemically extracted oil and its incompatibility with traditional Indian high-heat cooking methods. Instead of relying on a single “popular” oil, rotating different stable, nutrient-rich oils based on cooking needs is a smarter choice.
Even a small shift toward more stable fats can improve digestion, reduce inflammation, and support long-term metabolic health.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0